Published January 7, 2026
10 Best LMS and AI-Powered Learning Platforms in 2026
The Learning Management System (LMS) market is expanding rapidly, while buyer expectations are becoming more selective, skills-driven, and outcome-focused.
The global LMS market is projected to grow from $28.58 billion in 2025 to $70.83 billion by 2030, reflecting a 19.9 percent compound annual growth rate. The broader global eLearning market is expected to reach $740.46 billion by 2032, up from $227.34 billion in 2023. Within this, the corporate LMS market alone is forecast to reach $50.1 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 23.8 percent.
At the same time, global EdTech investment declined to approximately $2.4 billion in 2024, the lowest level since 2015. This signals a shift away from growth-at-all-costs toward platforms that demonstrate operational efficiency, measurable outcomes, and long-term value. Despite reduced funding, adoption continues to rise, with nearly 995.9 million users expected to use eLearning platforms by 2029.
In North America, platforms such as Canvas, Blackboard, Moodle, and Brightspace continue to dominate higher education deployments, although market share varies by segment and methodology.
A major structural driver behind the rise of AI-powered learning platforms is workforce transformation. According to IBM research, approximately 40 percent of the global workforce will require reskilling due to AI and automation. This represents nearly 1.4 billion people worldwide, fundamentally reshaping how organizations evaluate learning platforms.
What is an LMS?
A Learning Management System (LMS) is software used to deliver, manage, track, and report learning and training programs. Modern LMS platforms support enrollment automation, learning paths, assessments, certifications, analytics, and governance across employees, customers, partners, and learners.
What is an AI-Powered Learning Platform?
An AI-powered learning platform extends the traditional LMS by using artificial intelligence to accelerate content creation, personalize learning journeys, automate learning operations, and measure skill development.
Unlike traditional LMS platforms that primarily track course completion, AI-powered learning platforms focus on skills, readiness, and continuous upskilling, enabling learning to adapt to changing roles and business needs.
What Are the Key Features of an AI Learning Platform?
Organizations evaluating AI-powered learning platforms typically look for the following capabilities:
- AI-assisted content creation for courses, quizzes, and assessments
- AI tutors and knowledge assistants grounded in approved learning content
- Skills intelligence, including skills mapping, gap detection, and skill passports
- Personalized learning recommendations and adaptive learning paths
- Automation for enrollments, reminders, certifications, and compliance cycles
- Advanced analytics focused on proficiency, readiness, and performance
- Enterprise integrations with HRIS, CRM, collaboration tools, and APIs
- Governance, security, and role-based access control
- Mobile-first and multilingual learning delivery
- Support for extended enterprise learning such as customers and partners
Why Is an AI LMS Essential for the Global Skill-Based Future?
The global learning ecosystem is shifting from course-based training to skills-based capability development. AI accelerates this transition by shortening learning cycles and enabling continuous reskilling.
IBM research highlights that nearly 40 percent of workers will require reskilling due to AI-driven role changes, with entry-level roles experiencing the earliest impact. Organizations that invest effectively in reskilling consistently outperform peers in productivity, adaptability, and long-term growth.
As a result, modern LMS platforms are evolving into systems of record for skills, capability development, and workforce readiness.
How Are AI LMS Platforms Transforming Learning Globally?
Across regions, AI-powered LMS platforms are reshaping learning delivery in consistent ways:
- Guided learning journeys replacing static content libraries
- Skill evidence and proficiency tracking replacing basic completion metrics
- Automated learning operations reducing manual administration
- Personalized learning aligned to real work contexts
- Deep integration with workplace tools and enterprise data systems
In regions such as MENA, platforms offering robust Arabic language support, RTL interfaces, and enterprise-grade governance are increasingly differentiated.
LMS & AI-Powered Learning Platforms Comparison (2026)
| Platform | Best For | AI Capabilities | Skills Focus | Learning Models Supported |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blend-ed | Training companies, professional academies, enterprise upskilling | AI course creation, AI tutor, AI skill gap detection, AI knowledge assistant | Strong skills intelligence and readiness tracking | Self-paced, cohort-based, instructor-led, blended learning |
| 360Learning | SME-driven internal training | AI-assisted course creation, recommendations | Moderate, configuration-dependent | Self-paced, collaborative |
| Docebo | Large enterprises | AI discovery, personalization, GenAI workflows | Moderate to strong | Self-paced, blended, social |
| Absorb LMS | Compliance and extended enterprise | AI-powered admin workflows | Moderate | Self-paced, instructor-led |
| Sana | Knowledge-centric organizations | AI-native learning and knowledge assistants | Emerging | Continuous, self-directed |
| Disco | Cohort-based academies | AI-assisted creation, engagement tools | Limited | Cohort-based, community |
| LearnUpon | Customer and partner education | Limited AI, automation-focused | Low to moderate | Self-paced |
| CYPHER Learning | Skills-based operational training | AI assistants, automation | Moderate | Self-paced, blended |
| TalentLMS | SMBs and fast deployment | AI-assisted course creation | Limited | Self-paced |
| Disprz | Continuous upskilling | AI recommendations | Strong upskilling focus | Self-paced, mobile-first |
The 10 Best LMS Platforms & AI-Powered Learning Platforms (2026)
1) Blend-ed

Blend-ed is an AI-powered learning platform designed for organizations that deliver training as a core business, particularly training companies, professional academies, and education providers operating at scale. The platform brings together LMS, LXP, and AI authoring capabilities in a single system to support cohort-based programs, skills-focused learning, and multi-audience delivery.
Key Features
- Support for cohort-based, instructor-led, and blended learning programs
- AI Course Creator to accelerate course development from documents, SOPs, and training materials
- AI Tutor and Knowledge Assistant to support learners during courses and practice
- Skills analytics and AI-driven skill gap detection across programs and cohorts
- Role-based onboarding and structured learning journeys
- Monetization and paid program support for academies and training providers
- Multilingual delivery with strong Arabic-first and RTL support
- Centralized analytics across learners, cohorts, and programs
- Mobile-first learning experience for distributed audiences
Pros
- Well suited for training companies and professional academies managing multiple programs, cohorts, or client organizations
- Unified platform covering content creation, delivery, and skills tracking
- Strong multilingual capabilities, including Arabic and RTL experiences
- Flexible delivery models supporting self-paced, live, and blended formats
Cons
- Requires thoughtful configuration to align skills frameworks and analytics with business outcomes
- May offer more functionality than needed for organizations focused only on basic course hosting
Pricing
Subscription-based pricing
2) 360Learning
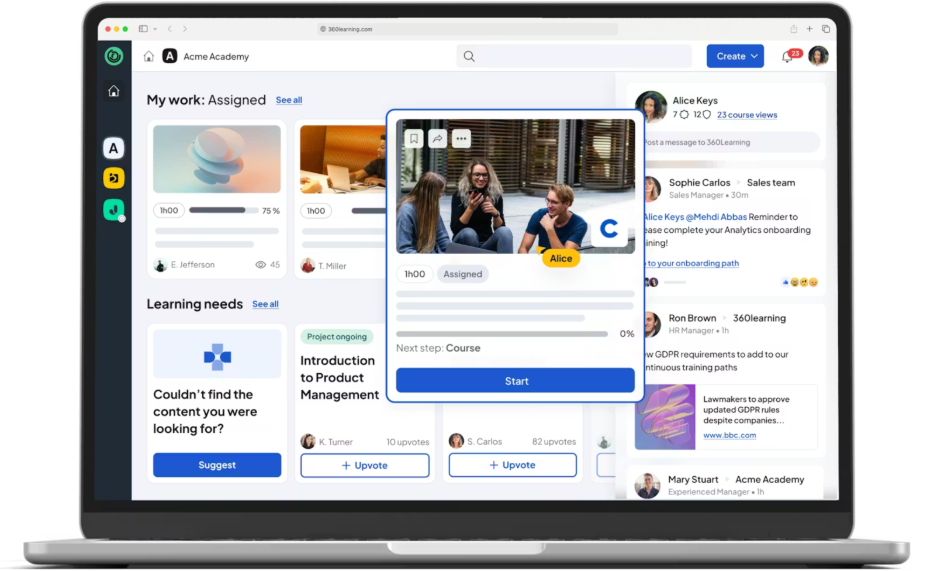
360Learning combines an AI-powered LMS with collaborative learning workflows that enable subject matter experts to co-create and improve content.
Key Features
- AI-assisted course creation
- Collaborative authoring and feedback loops
- Automated LMS workflows
- Engagement analytics for internal learning
Pros
- Strong fit for SME-driven learning cultures
- Encourages decentralized knowledge sharing
Cons
- Extended enterprise and monetization use cases may require additional validation
- Skills intelligence depth varies by implementation
Pricing
Tiered per-user subscription pricing.
3) Docebo
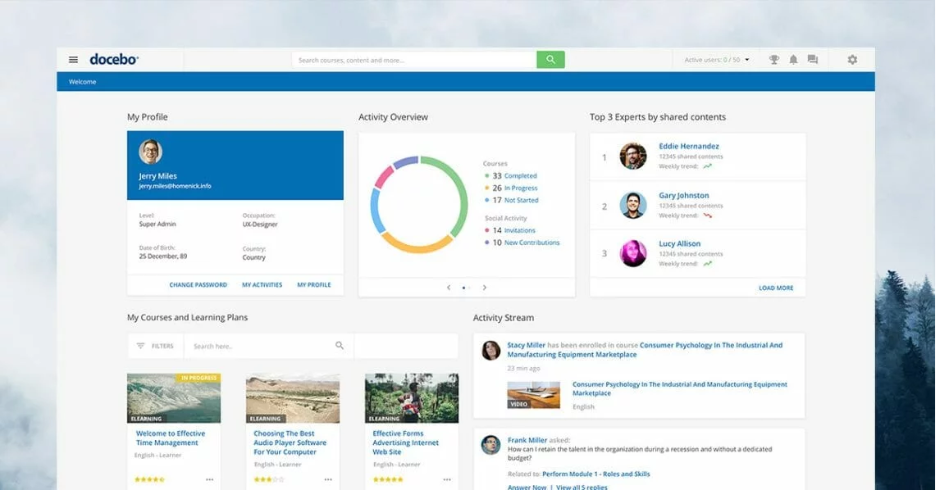
Docebo is an enterprise learning platform known for its breadth of AI-powered capabilities across content discovery, personalization, and automation.
Key Features
- AI-driven content recommendations and search
- Generative AI support for learning workflows
- Social and community learning tools
- Enterprise-grade integrations
Pros
- Mature enterprise ecosystem
- Strong automation and personalization capabilities
Cons
- Implementation complexity can be high
- Costs increase with additional modules and services
Pricing
Enterprise pricing based on user volume and selected modules.
4) Absorb LMS
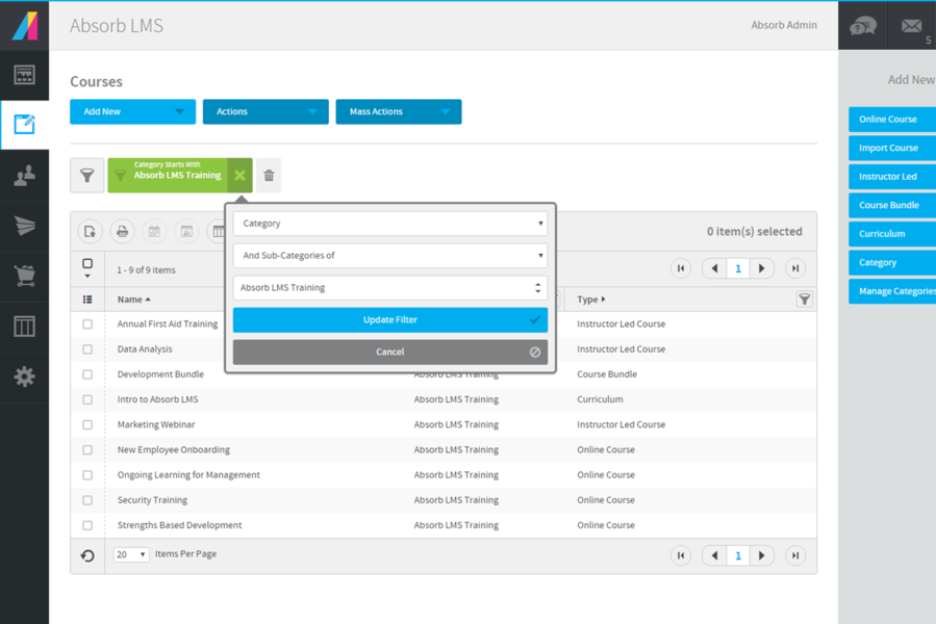
Absorb is a widely adopted LMS for training at scale, with AI capabilities under "Absorb Intelligence" and strengths in admin control, reporting, and extended enterprise needs.
Key Features
- AI-powered administrative workflows
- Observational checklists for skill validation
- Multi-tenant and eCommerce support
Pros
- Strong for compliance and operational training
- Suitable for extended enterprise learning
Cons
- AI depth varies by plan
- Skills-first analytics require careful evaluation
Pricing
Custom pricing based on scale and features.
5) Sana
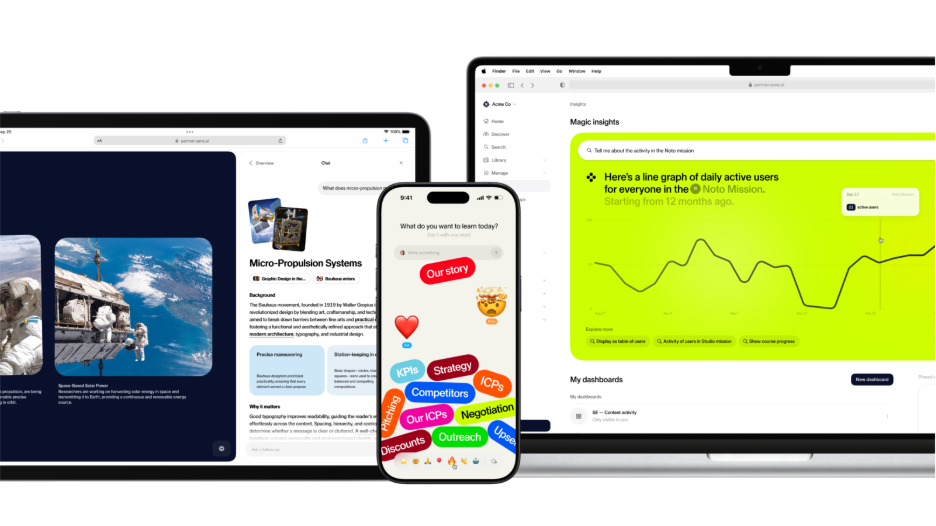
Sana positions itself as an AI-native learning and knowledge platform, leaning heavily into AI-first experiences and "knowledge tools for work."
Key Features
- AI-first learning architecture
- Knowledge assistants for workplace learning
- Enterprise security and governance
Pros
- Strong alignment with learning in the flow of work
- Effective for knowledge-centric organizations
Cons
- Traditional LMS workflows may require customization
- Extended enterprise use cases should be validated
Pricing
Enterprise quote-based pricing.
6) Disco
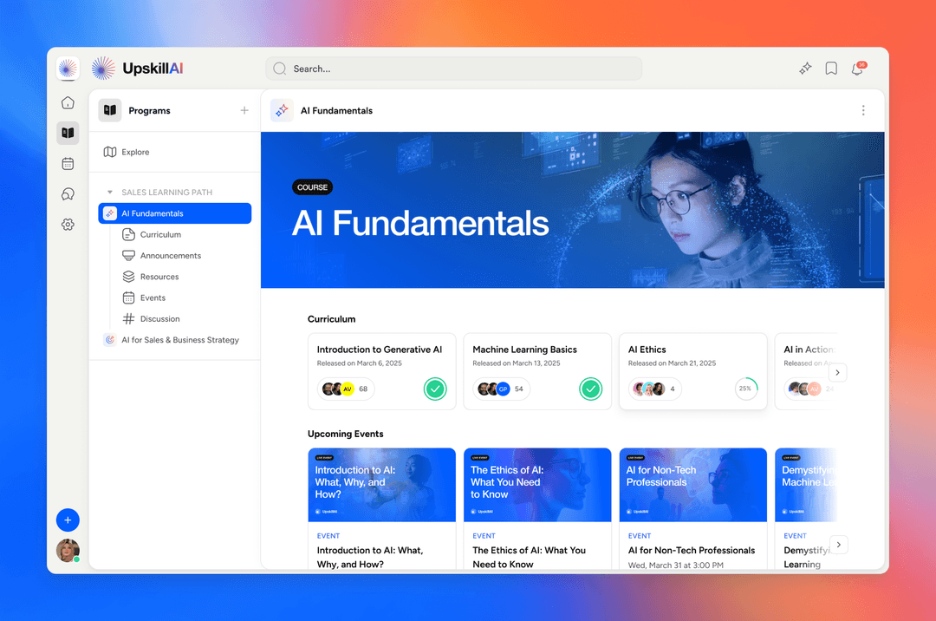
Disco is built for modern academies and cohort-based learning programs where community, events, and engagement matter as much as content.
Key Features
- AI-powered cohort learning tools
- Community engagement and events
- Social learning features
Pros
- Excellent for cohort and academy-based programs
- Strong learner engagement layer
Cons
- Governance and compliance depth should be validated
- SCORM-heavy ecosystems may face limitations
Pricing
Tiered SaaS pricing.
7) LearnUpon
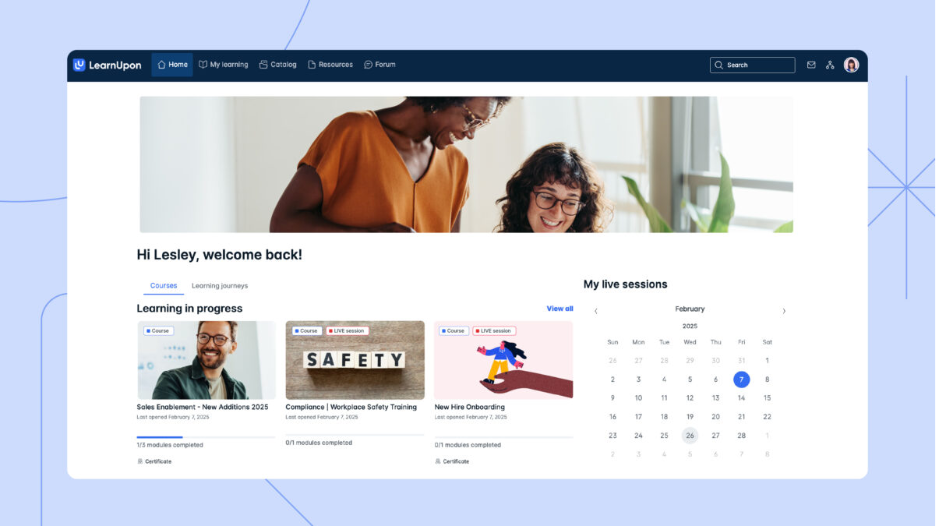
LearnUpon is a well-known LMS especially for customer training and extended enterprise scenarios, emphasizing reporting and integrations.
Key Features
- Customer education analytics
- CRM and enterprise integrations
- Multi-portal delivery
Pros
- Strong for customer and partner training
- Reliable reporting and integrations
Cons
- AI and skills intelligence depth varies
- Authoring depth depends on content strategy
Pricing
Tiered subscription pricing.
8) CYPHER Learning
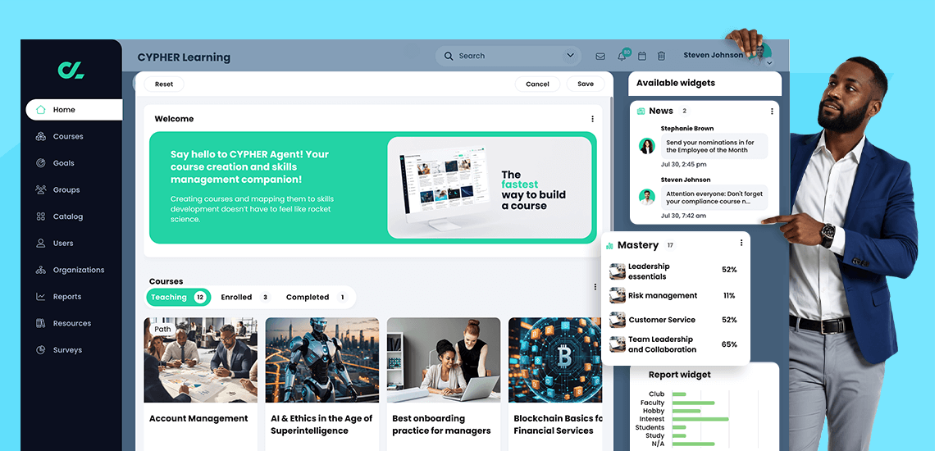
CYPHER positions as an all-in-one AI-powered learning platform with "agents" for creators, learners, and skills, plus automation capabilities.
Key Features
- AI learner assistants
- Workflow automation
- AI-supported course creation
Pros
- Balanced focus on automation and learner support
- Suitable for operational learning environments
Cons
- Enterprise governance requirements should be validated
- UX preferences vary
Pricing
Tiered SaaS pricing with enterprise options.
9) TalentLMS
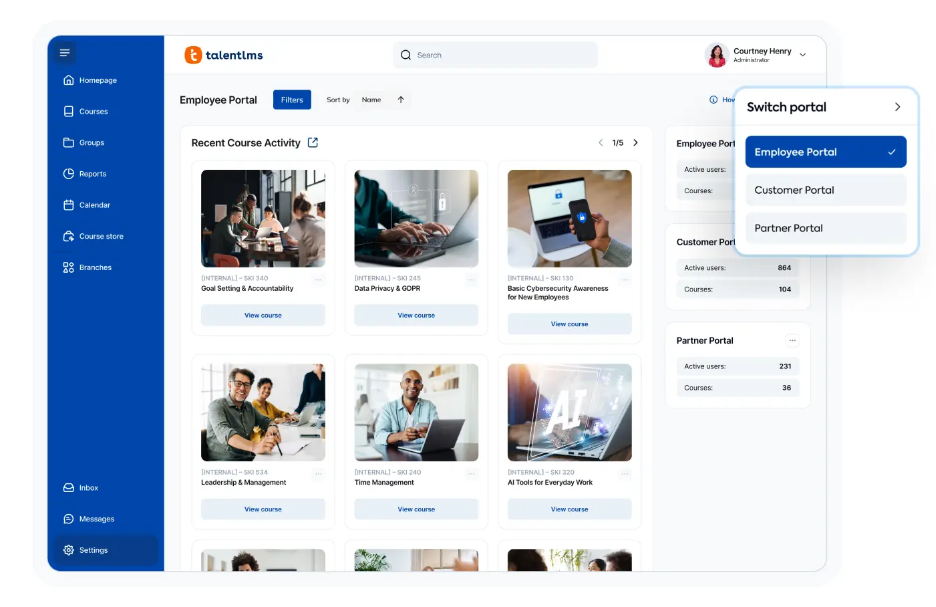
TalentLMS is popular for quick deployment and ease of use, increasingly adding practical AI features for course creation and workflow support.
Key Features
- AI-assisted course creation
- Gamification and engagement tools
- Built-in assessment generation
Pros
- Fast setup and intuitive UI
- Suitable for SMB and mid-market teams
Cons
- Limited depth for advanced skills intelligence
- Complex extended enterprise needs require validation
Pricing
Transparent tiered pricing.
10) Disprz
Disprz positions as a skills and learning platform focusing on upskilling/reskilling, with mobile-led learning experiences and AI-powered recommendations.
Key Features
- Centralized learning and onboarding
- AI-driven recommendations
- Mobile-led learning delivery
Pros
- Strong for upskilling and reskilling initiatives
- Effective for frontline and distributed teams
Cons
- Monetization and external training use cases require validation
- Skills frameworks should be aligned carefully
Pricing
Quote-based pricing.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing the Right AI LMS
Skills-first capability (not just course completion)
- Skill taxonomy support, skill extraction, skill passports
- Gap detection + role readiness dashboards
- Evidence tracking (projects, checklists, assessments, manager validation)
AI that's actually usable (not a demo feature)
- AI authoring that reduces time-to-publish
- AI tutor/assistant grounded in approved content (governance matters)
- AI recommendations that improve relevance, not noise
Operational automation (learning ops)
- Enrollment rules, reminders, re-certification cycles
- Cohorts + ILT scheduling if you run blended programs
- Admin workflows, approval flows, audit logs
Analytics that leadership trusts
- Cohort analytics, proficiency/readiness indicators
- Certification compliance reporting
- Exportable reports + API/BI integration options
Global readiness
- Localization depth (languages + RTL if relevant)
- Mobile performance (low bandwidth/offline options if needed)
- Accessibility + regional compliance expectations
Integrations and ecosystem fit
- SSO (SAML/OIDC), HRIS, CRM, Teams/Slack, Zoom
- Content standards: SCORM, LTI, xAPI (as needed)
- Clean APIs/webhooks for syncing data
Extended enterprise and monetization (if you train customers/partners)
- Multi-portal or multi-tenant structure
- E-commerce, coupons, invoices/VAT (region-specific needs)
- Segmentation: who sees what, when, and why
Total cost, implementation effort, and time-to-value
- What's included vs add-ons (AI, analytics, portals, content tools)
- Required services, onboarding, migration, configuration work
- Internal admin effort after go-live (ongoing ops)
Conclusion: Choosing the Right LMS or AI-Powered Learning Platform in 2026
The LMS and AI-powered learning platform landscape in 2026 reflects a market in transition. Traditional LMS platforms continue to play a critical role in compliance, structured learning delivery, and enterprise training operations. At the same time, AI-native and AI-enhanced platforms are redefining how learning is created, delivered, personalized, and measured.
Platforms like Docebo, Absorb, LearnUpon, and TalentLMS demonstrate how mature LMS vendors are integrating AI to improve automation, discovery, and administrative efficiency. These systems are well suited for organizations that prioritize stability, reporting depth, and predictable learning operations at scale.
Newer AI-forward platforms such as Sana, Disco, Disprz, and CYPHER Learning highlight a shift toward learning that happens closer to work, communities, and skills development. These platforms emphasize engagement, personalization, and continuous upskilling, often appealing to organizations rethinking learning beyond traditional course catalogs.
360Learning occupies a distinct position by combining LMS infrastructure with collaborative, SME-driven learning, making it effective for organizations that want to decentralize content creation while maintaining structure.
Blend-ed stands out for organizations whose core business revolves around training delivery itself, particularly training companies, professional academies, and education providers operating at scale. Its architecture brings together LMS, LXP, and AI authoring in a single system, with a strong emphasis on skills intelligence, cohort-based delivery, multilingual and Arabic-first experiences, and learning monetization. This makes it especially relevant for providers that must manage multiple programs, audiences, and clients while maintaining measurable learning outcomes.
Ultimately, there is no single "best" LMS or AI learning platform for every organization. The right choice depends on factors such as learning maturity, audience type, scale, skill requirements, delivery models, regional needs, and long-term learning strategy. As the market continues to grow and consolidate, buyers who evaluate platforms through a skills-first, outcome-driven, and operational lens will be best positioned to invest in learning systems that remain relevant over the next decade.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Which LMS platforms are best for organizations delivering training as a business?
LMS platforms designed for training companies and professional academies typically support cohort-based programs, instructor-led sessions, skills tracking across batches, multilingual delivery, and paid program management. These capabilities are essential when learning is a revenue-generating or client-facing activity rather than an internal HR function.
2. What is the difference between a traditional LMS and an AI-powered learning platform?
A traditional LMS focuses on course delivery, enrollment management, and completion tracking. An AI-powered learning platform extends this by enabling AI-assisted content creation, personalized learning recommendations, learner support through AI tutors, automation of learning operations, and skills-based analytics that go beyond completion metrics.
3. Do enterprises still need a traditional LMS in 2026?
Yes. Traditional LMS platforms remain relevant for compliance training, standardized onboarding, and regulated learning environments. However, many enterprises are now adopting AI-powered LMS platforms or hybrid systems to support continuous upskilling, role-based learning, and workforce readiness alongside compliance needs.
4. What features matter most when choosing an AI LMS?
Buyers should prioritize skills intelligence, practical AI capabilities that reduce manual work, automation of enrollments and certifications, analytics focused on readiness and proficiency, integration with HR and collaboration tools, and global readiness including mobile and multilingual support. Features should be evaluated based on outcomes rather than checklists.
5. Are AI-powered LMS platforms suitable for small or mid-sized teams?
Yes, provided the platform offers scalable pricing, ease of configuration, and clear time-to-value. Smaller teams often benefit from AI-assisted course creation and automation, but should avoid platforms that introduce unnecessary operational complexity or enterprise overhead.
6. How often should organizations reassess their LMS platform?
Most organizations should reassess their LMS every two to three years, or sooner if learning needs shift toward skills-based models, external training delivery, or large-scale reskilling initiatives. Rapid changes in AI capabilities and workforce requirements make periodic evaluation increasingly important.



